What Is Ménière Disease?
Ménière disease is a problem with the inner ear. It's also known as idiopathic endolymphatic hydrops. The inner ear is part of the ear responsible for balance as well as hearing. This condition is one of the most common causes of dizziness (vertigo) that starts in the inner ear.
Ménière disease affects the inner ear
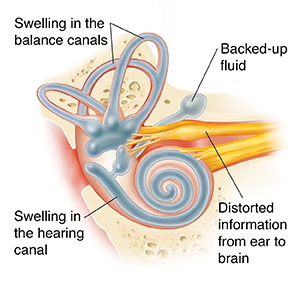
With Ménière, too much fluid (endolymph) backs up in the canals of the inner ear. The cause of this fluid backup is unknown. Extra fluid causes pressure to build up. The canals then swell and are unable to work correctly. Swelling in the hearing canal distorts or blocks sound information. Swelling in the balance canals distorts balance information. Distorted information travels from the inner ear to the brain. This causes problems with both balance and hearing. Ménière usually affects only one ear, but it can occur in both ears.
Symptoms of Ménière disease
-
Vertigo. This is a spinning or whirling sensation that causes balance problems. During a vertigo attack, you may have upset stomach (nausea), vomiting, and sweating. Attacks usually start suddenly and may last for 20 minutes to several hours. You may have attacks rarely, often, or in clusters. The first attack is usually the most intense.
-
Problems with hearing. Hearing is often partly or completely lost in the affected ear during vertigo attacks. It’s common for hearing to gradually get worse as the illness goes on.
-
Tinnitus. This is when you have ringing, buzzing, whistling, or roaring noises in the affected ear. These noises may come and go or may always be present. The noises may get louder just before a vertigo attack.
-
A feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear. This is sometimes felt most strongly right before a vertigo attack.
You may feel fine between attacks. Or your hearing or balance problems may continue between attacks.
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.